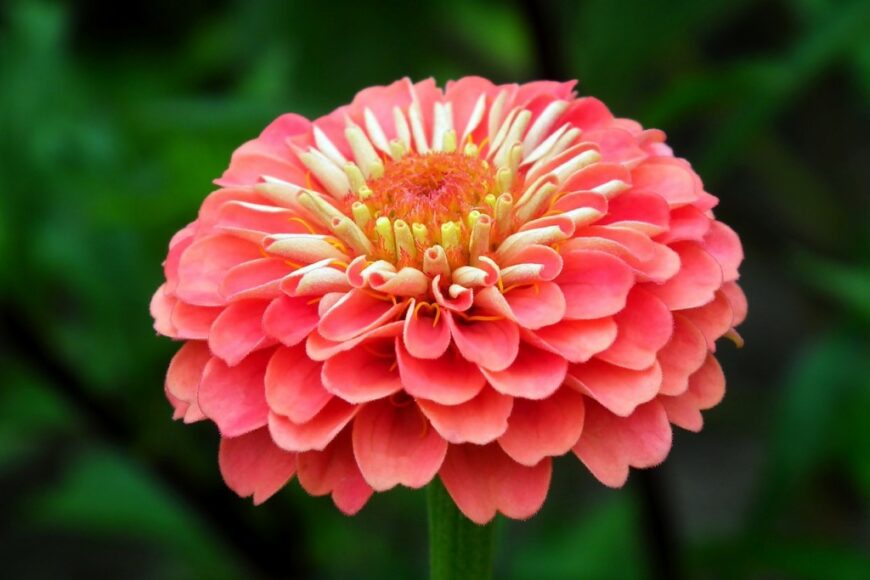

 Name: Zinnia
Name: Zinnia Family: Asteraceae
Family: Asteraceae Origins: Southwestern United States and Mexico
Origins: Southwestern United States and Mexico Humidity: Prefers moderate humidity levels, but can tolerate dry conditions.
Humidity: Prefers moderate humidity levels, but can tolerate dry conditions. Location: Full sun to partial shade.
Location: Full sun to partial shade. Soil: Well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral or slightly acidic pH.
Soil: Well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral or slightly acidic pH. Pests and diseases: Common pests include aphids, thrips, and slugs. Common diseases include powdery mildew, leaf spot, and stem rot.
Pests and diseases: Common pests include aphids, thrips, and slugs. Common diseases include powdery mildew, leaf spot, and stem rot. Care: Water regularly, but avoid overwatering. Fertilize every 2-3 weeks with a balanced fertilizer. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage more blooms.
Care: Water regularly, but avoid overwatering. Fertilize every 2-3 weeks with a balanced fertilizer. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage more blooms. Height of growth: Zinnias can grow anywhere from 6 inches to 4 feet tall, depending on the variety.
Height of growth: Zinnias can grow anywhere from 6 inches to 4 feet tall, depending on the variety. Planting in the soil: Plant zinnias outdoors after the last frost date. Space plants 6-18 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water deeply after planting.
Planting in the soil: Plant zinnias outdoors after the last frost date. Space plants 6-18 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water deeply after planting.Zinnias, beloved for their vibrant colors and easy cultivation, belong to the Asteraceae family. Originating from the American Southwest, Mexico, and South America, these annuals have become a favorite among gardeners worldwide.
The Beauty of Zinnias
Zinnias come in a plethora of colors, shapes, and sizes, from dainty dwarf varieties to large, double-flowered cultivars. Their ability to attract butterflies and beneficial insects makes them a valuable addition to any garden.
Content:
Growing Zinnias: A Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the Right Zinnia Variety
When choosing zinnias for your garden, consider factors such as size, color, and purpose. Popular varieties include the classic Zinnia elegans, the compact Zinnia angustifolia, and the striking Zinnia haageana.
Ideal Growing Conditions
Zinnias thrive in full sunlight, requiring at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Well-drained soil with a pH between 5.5 and 7.5 is optimal for their growth.
Soil Preparation
Prepare the soil by incorporating organic matter like compost to improve fertility and drainage. Zinnias are adaptable but perform best in soil with good aeration.
Planting Zinnias: A Step-by-Step Guide
Sowing Zinnia Seeds
- Timing: Plant zinnia seeds after the last frost when the soil has warmed.
- Spacing: Follow packet instructions for proper spacing, generally 6 to 24 inches depending on the variety.
- Depth: Plant seeds about ¼ inch deep in well-prepared soil.
Transplanting Zinnia Seedlings
- Timing: Transplant seedlings when they have at least two sets of true leaves.
- Spacing: Maintain proper spacing to allow for adequate air circulation.
- Watering: Water transplants thoroughly after planting to reduce transplant shock.
Zinnia Care Tips
Watering
- Regular Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during dry periods.
- Avoid Overhead Watering: Water at the base to prevent foliar diseases.
Fertilizing
- Balanced Fertilizer: Apply a balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season.
- Avoid Excess Nitrogen: Too much nitrogen can result in lush foliage at the expense of flowers.
Deadheading
- Promote Blooming: Pinch off spent flowers to encourage continuous blooming.
- Seed Harvesting: Allow some flowers to go to seed for future planting.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Common Pests
Zinnias are generally resistant to pests, but occasional issues include aphids, spider mites, and caterpillars. Neem oil or insecticidal soap can be effective remedies.
Disease Prevention
Proper spacing, good air circulation, and avoiding overhead watering help prevent foliar diseases like powdery mildew.
Zinnias as Companion Plants
Zinnias are excellent companion plants, attracting pollinators and beneficial insects. Interplant them with vegetables to enhance biodiversity and promote a healthy garden ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can zinnias tolerate partial shade?
Zinnias thrive in full sunlight, but they can tolerate some light shade. However, for optimal flowering, it’s best to provide them with as much sunlight as possible.
Q2: How do I prevent powdery mildew on zinnias?
To prevent powdery mildew, ensure good air circulation, avoid overcrowding, and water at the base of the plants. Applying fungicides preventatively can also be beneficial.
Q3: Can I grow zinnias in containers?
Yes, zinnias can be grown in containers. Choose dwarf varieties and use well-draining potting mix. Ensure the containers have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
Q4: When is the best time to harvest zinnia seeds?
Harvest zinnia seeds when the flower heads have dried on the plant. Remove the seeds and store them in a cool, dry place for future planting.
Q5: How can I attract more butterflies to my zinnia garden?
Planting a variety of zinnias in different colors and sizes, along with providing other nectar-rich flowers, will attract butterflies to your garden.

