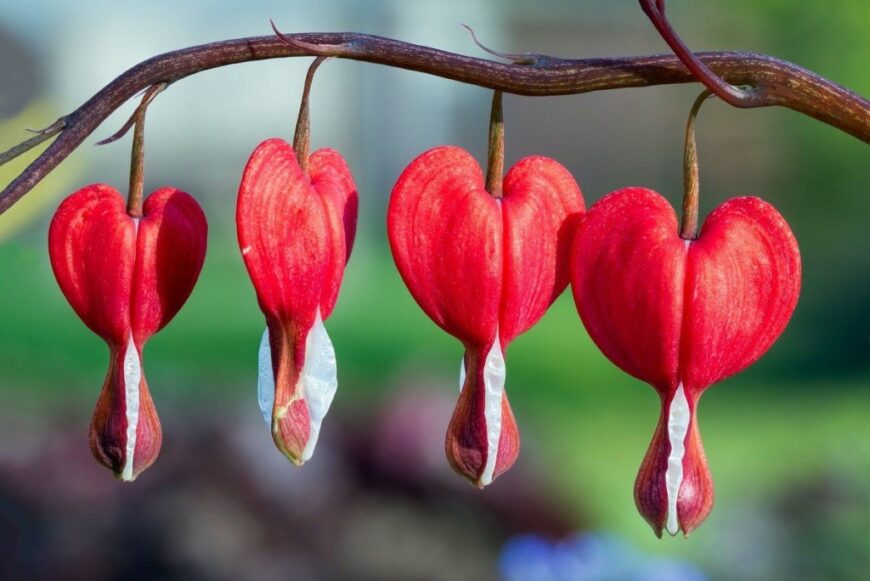

 Name: Bleeding Heart
Name: Bleeding Heart Family: Fumariaceae
Family: Fumariaceae Origins: Eastern Asia and North America
Origins: Eastern Asia and North America Humidity: Prefers moist soil and humid environments.
Humidity: Prefers moist soil and humid environments. Location: Partial shade to full shade.
Location: Partial shade to full shade. Soil: Well-drained, fertile soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH.
Soil: Well-drained, fertile soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. Pests and diseases: Common pests include aphids, slugs, and snails. Common diseases include leaf spot, fungal diseases, and nematodes.
Pests and diseases: Common pests include aphids, slugs, and snails. Common diseases include leaf spot, fungal diseases, and nematodes. Care: Water regularly, especially during hot weather. Fertilize every 2-3 weeks with a balanced fertilizer. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage reblooming. Mulch around the plant to conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
Care: Water regularly, especially during hot weather. Fertilize every 2-3 weeks with a balanced fertilizer. Deadhead spent flowers to encourage reblooming. Mulch around the plant to conserve moisture and suppress weeds. Height of growth: Bleeding hearts can grow anywhere from 12 to 36 inches tall, depending on the variety.
Height of growth: Bleeding hearts can grow anywhere from 12 to 36 inches tall, depending on the variety. Planting in the soil: Plant bleeding hearts outdoors in the fall or spring. Space plants 12-18 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water deeply after planting.
Planting in the soil: Plant bleeding hearts outdoors in the fall or spring. Space plants 12-18 inches apart, depending on the variety. Water deeply after planting. Blooming: Bleeding hearts typically bloom from late spring to early summer.
Blooming: Bleeding hearts typically bloom from late spring to early summer.The Bleeding Heart (Dicentra spectabilis) is a captivating perennial known for its heart-shaped flowers that dangle gracefully from arching stems. Native to Asia and North America, this shade-loving plant adds a touch of romance to any garden.
Content:
Choosing the Right Bleeding Heart Variety
Bleeding Hearts come in various cultivars, each offering unique features. ‘Alba’ boasts elegant white flowers, while ‘Gold Heart’ captivates with its golden foliage. Consider the specific characteristics that align with your garden design.
Planting Bleeding Hearts: A Step-by-Step Guide
a. Selecting the Right Location: Choose a shaded or partially shaded area with well-drained soil. Bleeding Hearts thrive in woodland settings and make excellent additions to shade gardens.
b. Soil Preparation: Enrich the soil with organic matter like compost. Bleeding Hearts prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil. Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
c. Planting Seeds or Transplants: Decide whether to start from seeds indoors or use transplants. Plant seeds or transplants according to package instructions, typically in early spring or fall.
Bleeding Heart Care Tips
a. Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during dry spells. Mulching helps retain moisture and keeps the roots cool.
b. Fertilizing: Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring. Avoid excessive nitrogen, as Bleeding Hearts prefer a moderate nutrient environment.
c. Mulching: Mulch around the base of the plants to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and provide a protective layer during winter.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Regularly inspect for pests like aphids and slugs. Use organic remedies such as neem oil or diatomaceous earth to deter pests. Ensure proper air circulation to prevent fungal diseases.
Companion Planting with Bleeding Hearts
Pair Bleeding Hearts with other shade-loving plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes. The contrasting foliage and textures create a visually appealing and harmonious garden.
Pruning Bleeding Heart Plants
Trim back faded flowers to encourage continuous blooming. Cut back the foliage after it turns yellow in late fall or early spring.
Benefits of Growing Bleeding Hearts in Your Garden
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, Bleeding Hearts contribute to a healthy garden ecosystem. Their shade tolerance and ability to attract pollinators make them valuable additions to any garden.

